

The router may need to be specially configured to provide this information via SNMP. So it works for both local and non-local subnets.
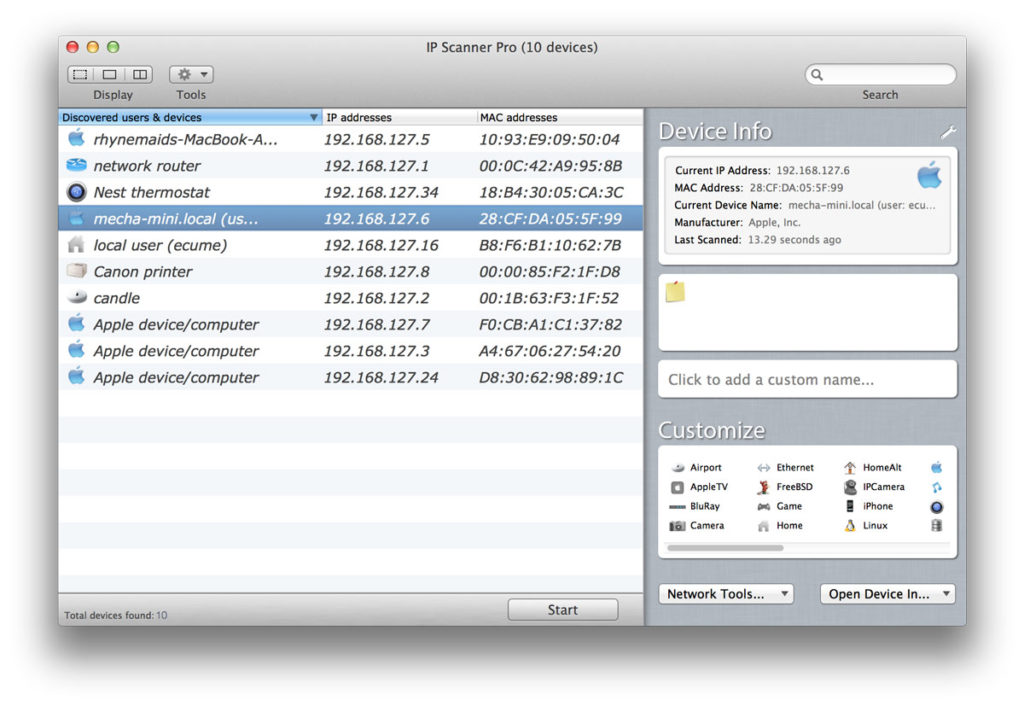
As the router sits between two subnets, it knows client MAC addresses on both sides. The downside here is that only the computers that support the NetBIOS protocol will respond with their MAC address. IP Scanner scans your local area network to determine the identity of all machines and Internet devices on the LAN. This method sends a special NetBIOS packet to the target computer, which works for both local and non-local subnets. The reason is that routers do not pass ARP messages from one subnet to another. This method always works in the local subnet, but it does not work with non-local subnets. A few devices that support NetBIOS will respond with their MAC address, but not all of them.Īs there is no single, universal method for resolving MAC addresses from a different subnet, Network Scanner has four relevant settings under Options – Program Options – Additional: You may still see some MAC addresses as the scanner attempts to use the NetBIOS protocol when ARP is not available. This is also why MAC addresses from a different subnet are not displayed.

The reason for that is the fact that a router residing between subnets cannot pass ARP traffic through. Scanning a different subnet is similar to scanning the local subnet, except the Address Resolution Protocol (ARP) used for resolving IP addresses to MAC addresses does not work across subnets.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
